Over many years of trading binary options, traders have developed various methods of managing trade size. The most popular among them is undoubtedly the Martingale strategy. However, many traders were not satisfied with its extremely high risk and ability to literally zero out an account in an instant. Therefore, an antipode of this system appeared - Anti-Martingale. In this review, we'll tell you what this system is, what are its advantages and disadvantages, and how to properly apply it for binary options trading.
Contents:
- Anti-Martingale: How to Turn the Game Upside Down?
- Double or Lose It All? Understanding the Parlay System
- How Not to Confuse Anti-Martingale, Parlay, and Express
- How to Apply Anti-Martingale Rules in the Market
- Building an Effective Trading System Based on Anti-Martingale
- Tips for Safe Use of Anti-Martingale in Binary Options
- Step-by-Step Guide to Applying Anti-Martingale in Practice
- Pros and Cons of Trading with the Anti-Martingale System
- Conclusion

Anti-Martingale: How to Turn the Game Upside Down?
Those who have been trading binary options for a long time have surely not only heard of but also repeatedly used the mega-popular capital management system among gamblers - Martingale. According to one version, its name is believed to come from the surname of an 18th-century London casino owner - John Henry Martingdale. Card game enthusiasts claim that it was thanks to Martingdale that this capital management system, where players increase their stake after a loss, gained wide popularity. Interesting, why was this beneficial for him? Write your opinion on this in the comments.
The Anti-Martingale system is the opposite of classic Martingale. Instead of increasing stakes after a loss, this method increases them after a win and decreases after a loss. It's precisely because of this principle that the prefix "anti" appears, which means "against" or "opposite."
Double or Lose It All? Understanding the Parlay System
The Anti-Martingale system has several variations, and one of the most famous is Parlay. Sometimes binary options traders confuse it with Anti-Martingale itself, although there are significant differences between them.
|
Characteristic |
Anti-Martingale |
Parlay |
|
Stake Changes |
Increases after winning, decreases after losing |
Increases after winning, remains unchanged after losing |
|
Goal |
Lock in profit after a series of winning trades and minimize losses after a series of losses |
Maximize profit during a "winning streak" |
|
Risks |
Risk of prolonged drawdown if a series of losses follows after increasing the stake |
Risk of large drawdown due to inability to reduce stakes during a series of losing trades |
As seen from the table above, the main difference between these capital management approaches lies in changing the stake after a loss. Anti-Martingale suggests reducing it, while Parlay suggests going all-in, relying on the player's "winning streak": three, seven, ace... well, you get the idea.
How Not to Confuse Anti-Martingale, Parlay, and Express
Often in betting and trading, you can encounter terms: Anti-Martingale, Parlay, and Express. Typically, they all appear in the context of capital management methods discussions, and they are unfairly confused with each other. In fact, these concepts describe completely different approaches and money management strategies in binary options trading.
|
Characteristic |
Anti-Martingale |
Parlay |
Express |
|
Type |
Capital management strategy |
Bet type |
Bet type (often synonymous with Parlay) |
|
Goal |
Profit locking, loss minimization |
High profit through coefficient multiplication |
High profit through coefficient multiplication |
|
Risk |
Extended drawdown |
High probability of losing entire express |
High probability of losing entire express |
|
Events |
One event at a time |
Multiple events in one bet |
Multiple events in one bet |
How to Apply Anti-Martingale Rules in the Market

Before using the Anti-Martingale system, it's necessary to determine the initial stake size and the multiplier by which it will increase in case of profit. As known, one should start small, so the minimum investment size of $1 at binary options broker Pocket Option is quite sufficient.
It's particularly important to note that no money management technique can turn a losing trading system into a profitable one. Therefore, before using any capital management systems, it's important to choose a strategy or indicators for generating trading signals. We also draw your attention to our free signals service, which you can learn more about in the article "WinOptionSignals Review".
To save time on additional calculations, we recommend using the Anti-Martingale calculator right on our website.
Building an Effective Trading System Based on Anti-Martingale

Uncontrolled and unlimited increase in stake size in case of a long series of profitable trades sounds good only in theory. In practice, this often leads to one losing operation with a large volume potentially destroying the results of all previous trades.
To reduce the destructive and extremely painful psychological effect of such an event, experienced traders recommend modifying the basic Anti-Martingale algorithm by adding a limit on the number of consecutive increases. For example, after three consecutive increases, the trader can switch to trading with a fixed minimum volume to avoid losing all previously accumulated profit in one losing trade:
First trade — $1.
Second trade — $1 + $1 = $2.
Third trade — $1 + $1 + $1 = $3.
After three consecutive winning trades, it's recommended to return to the initial stake of $1 until the first loss, after which the cycle begins anew. Note that in this example, the multiplier equals the initial stake of $1, which corresponds to a conservative approach.
Tips for Safe Use of Anti-Martingale in Binary Options
To get the most out of this methodology's positive properties, certain rules and general recommendations should be followed:
- Trade volatile instruments with clearly defined trends.
- Trade exclusively during active market hours.
- Don't enter trades before the publication of important macroeconomic data, which can be known in advance from the economic calendar.
- Choose only options with a payout of at least 75%.
- Monitor the percentage of profitable trades in your trading strategy. If this indicator falls below 60%, consider changing your trading methodology.
Step-by-Step Guide to Applying Anti-Martingale in Practice
Now let's look at the effectiveness of the Anti-Martingale system using a specific example. On the graph below, numbers indicate trades according to one of the trading systems described on our website. In this case, what's important is not where and when we opened trades, but with what volume we did it.
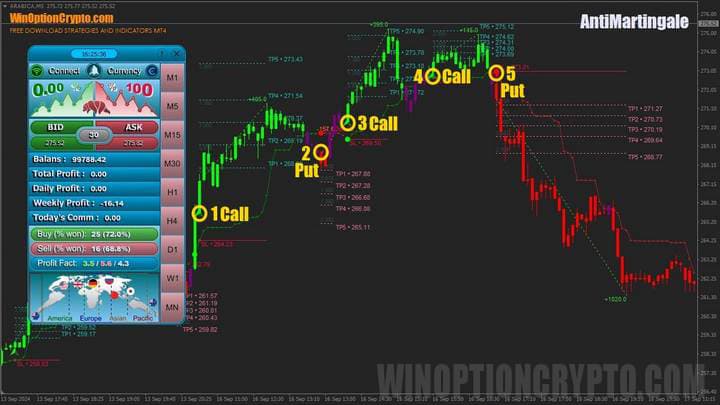
For simplicity of the experiment, let's choose the initial stake size and multiplier equal to $1. This means that after each profitable trade, we will increase the stake by $1, and in case of a loss - start trading with the initial stake. Let's assume that the payout percentage for trades is 75%.
Trade 1
After our trading system's signal appears, we buy a Call option for $1 with a 3-candle expiration period. The trade closes with profit, we earned $0.75.
Trade 2
A downward signal appeared - we open a Put option for $2, since the previous trade was profitable and according to our rules, we should increase the trading volume by the multiplier equal to $1. The market didn't go in our direction and we record a loss of $2.
Trade 3
A signal to buy Call appeared. Considering the loss in the previous trade, we open a new position with the initial stake size - $1. The trade brings profit of $0.75.
Trade 4
We buy Call for $2, since we got profit in the previous trade. The trade brings profit again, but now of $1.50.
Trade 5
In the last trade of our experiment, we buy Put for $3, since we got profit in the previous trade. The trade brings profit again, now of $2.25.
In total, on this series of 5 trades using the Anti-Martingale system, we earned: 0.75 - 2 + 0.75 + 1.5 + 2.25 = $3.25. It's interesting to note that if we had used 2 as the multiplier instead of the initial stake size, the result would differ only in the last trade.
Pros and Cons of Trading with the Anti-Martingale System
Pros of Anti-Martingale:
- Less risky than Martingale.
- With a long series of profitable trades, as our experiment showed, profit can grow very quickly.
- After a series of losing trades, it fairly quickly compensates for previous losses.
- The system rules are relatively simple and don't require deep knowledge of mathematics or statistics.
Cons of Anti-Martingale:
- Risk of losing the deposit is higher than when using fixed risk per trade.
- Not suitable for long-term trading, as the probability of a series of losing trades significantly increases over time.
- Longer deposit recovery compared to the Martingale system.
Conclusion
Thus, the Anti-Martingale system is a method of capital management where the stake size increases after each profitable trade and decreases after a loss. Without delving into details, this approach might seem like a very attractive way to increase deposits. However, like any other money management methodology, Anti-Martingale has its pros and cons.
It's important to remember that even when used correctly, this strategy doesn't guarantee success in the long term, and in case of a series of failures, the trader may face significant losses. To minimize risks, we recommend combining Anti-Martingale with a reliable strategy and disciplined approach to trading itself.
See also:
How to Make Money on Binary Options
Pros and Cons in Binary Options Trading



To leave a comment, you must register or log in to your account.